 PA Media
PA MediaThe government has outlined plans to tackle England’s housing shortage, with local councils given targets for new homes in their area.
Housing Minister Matthew Pennycook said the focus is on areas where housing is least affordable.
How many new homes does the government want?
The aim is for 370,000 new homes in England every year, to fulfil a government promise for 1.5m new homes within the next five years.
Local authorities are being told to give developers permission to build.
Millions of people can’t afford to buy their first home and there is a backlog of people living in unsuitable accommodation.
According to the government, 1.3 million households are on social housing waiting lists and a record number – including 160,000 children – are in temporary accommodation.
The government, which announced its plans in the updated National Planning Policy Framework, has not set a date for when the 370,000 target will be reached.
Where will new homes be built?
Areas with the most unaffordable housing but the greatest potential for growth have higher housebuilding targets, the government says.
Housing minister Matthew Pennycook told the Commons the government will be “focusing growth on city regions”.
He said London will see its annual quota as a whole set to around 88,000.
That’s around 10,000 less than the target under the previous Conservative government. However, there are variations within the capital, with some areas being given higher targets.
For example, Kensington and Chelsea is being asked to build 5,107 new homes – up from 1,381. The target for Westminster is 4,341 – up from1,862.
The South East as a whole will have an annual quota of almost 71,000 – 20,000 more than planned under the former Conservative government.
Other notable changes include:
- South Oxfordshire – rising from the Conservative’s target of 579 to 1,242
- Winchester – rising from 676 to 1,157
- Bath and North East Somerset – rising from 717 to 1,471
- Warwick – rising from 653 to 1,062
- Warrington – rising from 791 to 1,064
- Cumberland – rising from 244 to 1,105
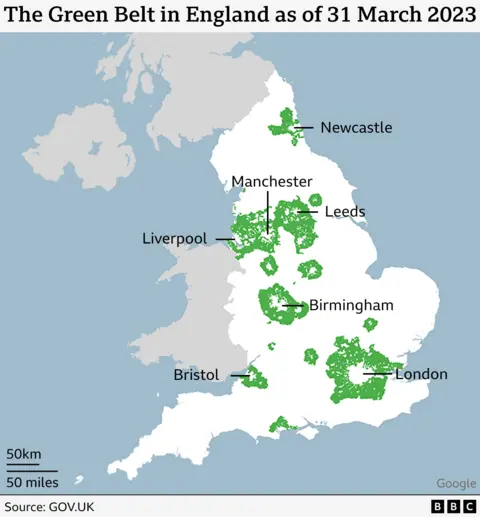
Will the green belt be developed?
Previously developed land will be prioritised for new homes, the government says. These “brownfield sites” can include places like derelict industrial or commercial developments.
However, Pennycook said brownfield land alone will not be enough to deliver the number of homes the country needs.
As a result, councils will also be ordered to review green belt boundaries – which were created to prevent urban sprawl – by identifying lower quality “grey belt” land that can be built on.
The government has previously described the grey belt as “poor quality and ugly areas” on the green belt.
It has previously given an example of grey belt land as a disused garage in Tottenham, north London, which could not be built on because it was within the green belt.
There is no official data on the size of the grey belt.
However, estate agent Knight Frank previously carried out its own research and identified 11,000 previously developed sites – making up less than 1% of the green belt.
These were concentrated in the south of England, with just over 40% within the London green belt area.
They estimated that 100,000-200,000 new family homes could be built on grey belt sites.
Prime Minister Sir Keir Starmer said development would be locally led, with the land developed “brownfield first, grey site next, and greenbelt last”.
Conservative shadow housing secretary Kevin Hollinrake said: “This planning framework pushes development to rural areas, concreting over green belt, green fields and over our green and pleasant land.”
Will new homes be affordable and have services?
Announcing its plans, the government said councils and developers must give greater consideration to social rent when building new homes.
It said local leaders will have “greater powers to build genuinely affordable homes for those who need them most”.
The definition of affordable homes includes homes for sale as part of a shared-ownership scheme, or those rented at a lower rate, or as part of a social housing agreement.
Any development on green belt must meet strict requirements, with developers having to provide infrastructure for local communities, such as nurseries, GP surgeries and transport, the government said.
How will house-building targets be reached?
Prime Minister Keir Starmer said planning decisions will be pushed through if necessary.
“The starting point is local plans, and that’s really important for councils to develop the plan according to the target, taking into account local need, and working with developers. So that’s where it starts,” he said.
“But are we going to push it though if those plans don’t work? Yes, yes we absolutely are.”
Responses from local councils to an Freedom of Information request by the BBC suggest the government could be on a collision course with local authorities.
The vast majority of councils expressed concern. Many fear targets have not taken into account strains on local infrastructure, land shortages, and a lack of capacity in the planning system and construction industry.
According to the latest report from the Construction Skills Network, around 225,000 new construction workers are needed across the UK by 2027.
Why build homes when others are standing empty?
There are just under 700,000 empty and unfurnished homes in England, according to the most recent government figures.
Of those, 261,471 are classed as “long-term empty,” meaning no-one has lived there for six months or more.
But bringing derelict and abandoned properties back to life can be a long and complex process.
Even finding out who owns properties that have been standing empty for years, or in some cases decades, can be a challenge.
